Modern front-end applications are no longer limited to simple user interfaces. They power mission-critical workflows, handle sensitive data, and integrate with complex backend ecosystems. As applications scale, challenges related to security, maintainability, and performance become more visible. Organizations now expect front-end systems to be resilient, structured, and easy to evolve without constant rewrites.
To meet these expectations, many technology leaders choose Angular for enterprise-grade applications. When businesses hire Angular developers, they are not just adding UI expertise to their teams; they are bringing in professionals who understand architecture, security boundaries, and long-term maintainability.
Understanding the Role of an Angular Developer
An Angular developer is responsible for designing, developing, and maintaining front-end applications using the Angular framework. Their work goes beyond building components and views; they shape how the application is structured, how data flows, and how the system responds to changes over time.
Core Responsibilities:
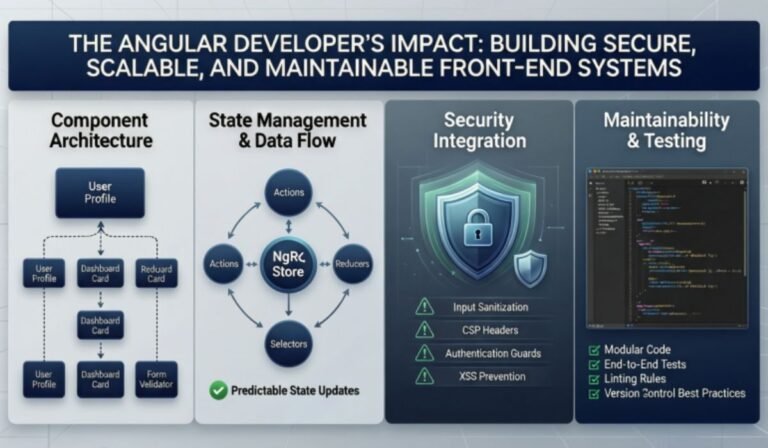
- Modular Architecture: Creating reusable components and feature modules.
- State Management: Handling complex data flows and application logic.
- API Integration: Collaborating with backend engineers to align on API contracts.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Working with UX designers on design systems and DevOps teams for deployment workflows.
Strong Angular developers are proficient in TypeScript, RxJS, and the Angular CLI. This combination of technical depth and collaboration makes their role essential in modern product teams.
Angular Framework Overview for Enterprise Applications
Angular is designed with large-scale applications in mind. Its opinionated structure encourages consistency across teams and projects, which is particularly valuable when multiple developers contribute to the same codebase over long periods.
The framework’s modular architecture allows applications to be divided into feature modules, making code easier to navigate. Built-in tooling, such as dependency injection and strict typing, helps teams manage complexity without sacrificing readability. Furthermore, Angular offers predictable release cycles and long-term support (LTS) options, allowing organizations to plan upgrades strategically.
Building Secure Front-End Systems with Angular
Angular’s Built-in Security Mechanisms
Security is a foundational concern. The framework includes built-in protections against common vulnerabilities like Cross-Site Scripting (XSS). Angular automatically sanitizes values used in templates and enforces safe binding practices by default.
Authentication and Authorization
Angular developers implement secure authentication flows by integrating identity providers and managing access tokens. Route guards are commonly used to enforce role-based access control, ensuring users only access authorized views.
Secure API Communication
Front-end applications rely heavily on APIs. Angular developers use HTTP interceptors to:
- Attach authentication headers (like JWT).
- Handle errors centrally.
- Enforce security policies consistently across all requests.
Ensuring Maintainability in Angular Applications
Modular and Scalable Architecture
Maintainability starts with the separation of concerns. Feature modules and lazy loading allow teams to scale applications without turning them into monoliths. A clean project structure reduces the risk of unintended side effects when features evolve.
Code Quality and Best Practices
Developers use TypeScript to enforce type safety and reduce runtime errors. Clear interfaces and well-defined services improve readability. Additionally, linting and formatting tools help enforce coding standards across distributed teams.
State Management and Data Flow
As applications grow, managing state becomes complex. Angular developers use RxJS to create predictable data streams. In larger applications, specialized state management libraries may be introduced to centralize data handling and maintain clarity.
Performance Optimization and Long-Term Stability
Optimization Impact
Performance and maintainability are linked. Developers optimize change detection strategies to reduce unnecessary re-rendering. Smaller, well-organized bundles created through code splitting are easier to debug and scale gracefully.
Testing and Debugging
Testing is essential for stability.
- Unit Tests: Validate individual components and services.
- End-to-End (E2E) Tests: Ensure entire user flows work as expected. Well-tested codebases reduce the risk of regressions during updates or refactoring efforts.
Keeping Applications Up to Date
Understanding Angular’s release cycles allows teams to benefit from performance and security improvements without breaking existing functionality. Regular dependency updates keep applications compatible with modern browser standards.
Best Practices Summary
Successful Angular development requires a security-first mindset. Key practices include:
- Staying informed about evolving web threats.
- Maintaining clear documentation and shared knowledge.
- Conducting thorough code reviews.
- Prioritizing thoughtful architecture over delivery speed.
When organizations hire AngularJS developers or modern Angular specialists, they should look for professionals who value maintainability as a core pillar of development.
Conclusion
Angular developers play a critical role in building systems that are secure, scalable, and easy to maintain. By leveraging the framework’s built-in features and following structured design principles, they create applications that support growth, protect users, and adapt smoothly to future requirements.